Everything you ever wanted to know about windows
Windowpedia
What is a Window?
A Window is an aperture or opening in the wall, whose main functions are ventilation, ingress of natural light and a view of the outside world. A window, however, is often plagued by concerns such as rainwater leakage, dust ingress, sound inundation, bugs, and fly’s entry from the outside. Modern technology and materials of windows – do address the above perturbations along with providing high aesthetics, ease of operation, less or no maintenance and long life of the system.
A window, in a modern building, is the only system which operates both inside and outside. Hence the performance parameters of a window are measured from both sides.
A window is also an intrinsic architectural component which defines the mood, view and operational value of a room and building. The profuse designs, shapes, styles, finishes available in modern window help add texture and life to the building.

What are the different materials used for Window manufacture?
Improving the thermal resistance of the frame can contribute to a window’s overall energy efficiency, particularly its U-factor. There are advantages and disadvantages to all types of frame materials, but vinyl, wood, fiberglass, and some composite frame materials provide greater thermal resistance than metal.
uPVC Frames – Vinyl window frames are usually made of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) with ultraviolet light (UV) stabilizers to keep sunlight from breaking down the material. uPVC window frames do not require painting and have good moisture resistance. The hollow multichambered profiles of these frames are great Thermal insulators. The property of the material makes it dust proof, sound attenuated and low maintenance with a high durability.
Aluminum or Metal Frames – Although extraordinarily strong, light, and almost maintenance free, metal or aluminum window frames conduct heat very rapidly, which makes metal an extremely poor insulating material. To reduce heat flow and the U-factor, metal frames should have a thermal break – an insulating plastic strip placed between the inside and outside of the frame and sash.
Wood Frames – Wood window frames insulate relatively well, but they require regular maintenance. Though, aesthetically premium these systems have effects of weathering conditions on them – they warp.
Composite Frames – Composite window frames consist of composite wood products, such as particleboard and laminated strand lumber, and some are mixed with polymer plastics. These composites are very stable, they have the same or better structural and thermal properties as conventional wood, and they have better moisture and decay resistance.
Fiberglass Frames – Fiberglass window frames are dimensionally stable and have air cavities that can be filled with insulation, giving them superior thermal performance compared to wood or uninsulated vinyl.
What are the different components of a Window?
The major components of a Window are divided into 4 major parts – the Frame, the Sash, the Glazing, and the Accessories.
The Frame and the Sash materials are generally made from the same materials. E.g., Wood, MS, Aluminium, or uPVC.
The Glazing part is that of Glass. With innumerable choice of options available – the glass specification is selected as per the technical and operational requirement of the building such Thermal Heat conduction, Natural lighting, and Noise attenuation.
The Accessories of the Window are majorly the Hardware used, the locking system, the handles, the hinges etc. Bug mesh and Random are other important inclusions of Accessories of a window.
Components of A Window
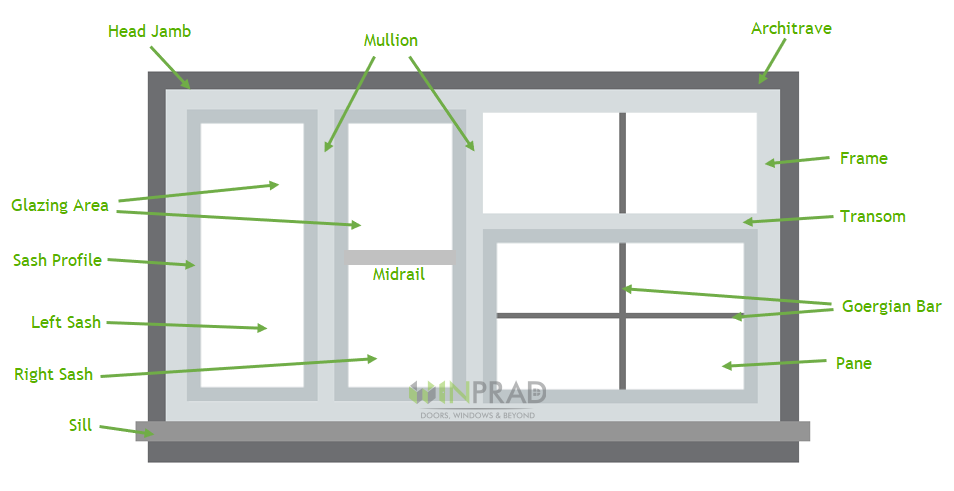
What are major Technical Terms in Window systems?
| Bay Window | A combination of three or more windows that projects outward from main walls forming a bay in a room, either square or polygonal |
| Casement Window | Windows with swinging open-able parts (Sashes) |
| Double Glazing | Use of two panes of glass in a window with a space in between |
| Extruded Profile | Sections made through the extrusion process |
| Extrusion | A process where solid plastics in the form of granules is melted in a heated chamber. The molten plastic is then forced out through a die and then immediately cooled to re-solidify to desired shape |
| Fusion Welding | A process where members are joined by heating the ends to create a semi solid area and fusing them together |
| Gasket | The black rubber strip that runs around the pane of glass in a window to create a weatherproof joint |
| Horizontal Slider | Windows/doors with sliding open-able panels (sashes) |
| Low ‘e’ glass | Refers to low emissivity glass. It lets in energy from the sun while preventing the heat escape from indoors to outdoors |
| Midrail | Dividers (horizontal or vertical) in a window/door sash |
| Mullion | Vertical dividers of window/door outer frame |
| Multi-point locking | A locking mechanism that locks at more than one point |
| Outer Frame | The part of the window fixed to the masonry work |
| Patio Door | A sliding glass door used in a patio area |
| Reinforcements | Steel or Aluminium sections are used in the chambers of the UPVC profile to provide necessary strength |
| Rollers | Wheels attached to the bottom of the sash of a window or door that allows it to slide easily |
| Sash | Open-able part of the window/door |
| Sill | The main horizontal part forming the bottom of the frame of a window |
| Single Glazing | Single glass in a window is called single glazing |
| Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC) | It measures how well a product blocks heat from the sun. SHGC is expressed as a number between 0 and 1. The lower the SHGC, the better a product is at blocking unwanted heat gain. |
| STC | Sound Transmission Class ‘Higher the STC rating, better is the sound insulation characteristic of the material |
| Tilt & Turn Window | A window that tilts at an angle for ventilation and opens inwards like a casement |
| Transom | Horizontal dividers of window/door outer frame |
| U’ Value | It is a measure of heat loss. Lower the ‘u’ value, better thermal insulation of the material |
| UPVC | Unplasticized polyvinyl chloride |
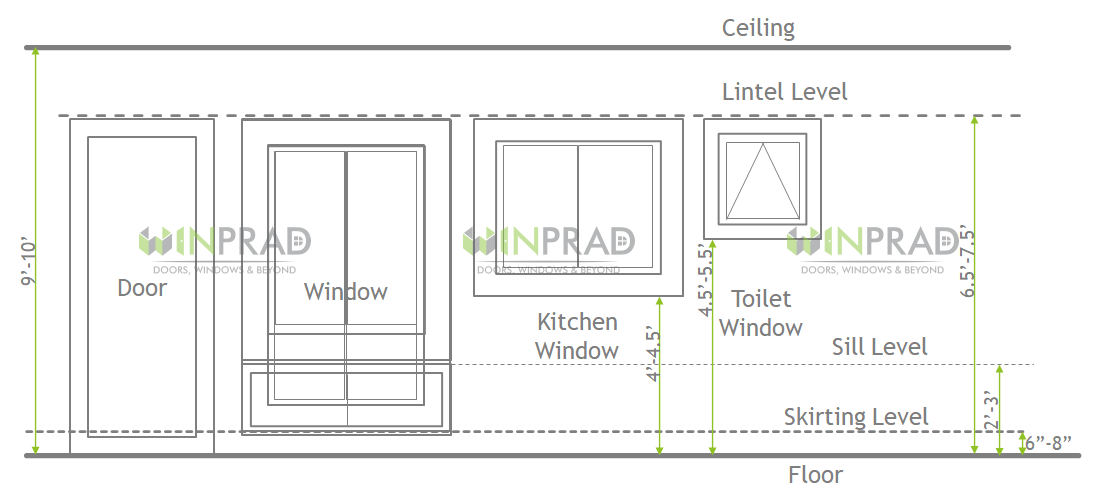
What are the major window systems in vogue?
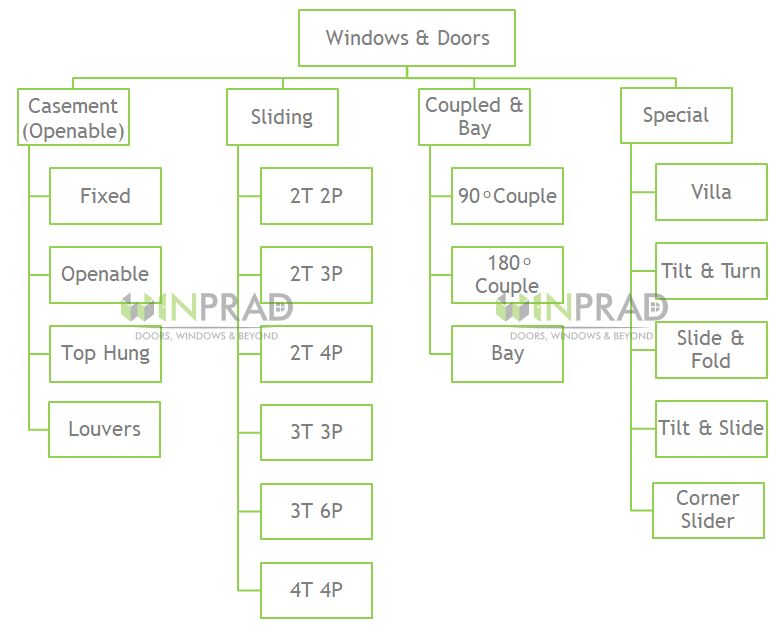
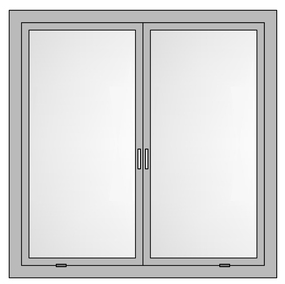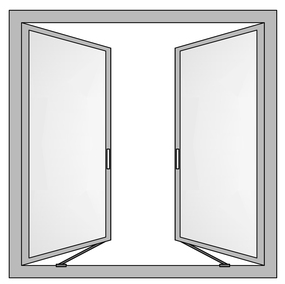
Casement Window
The oldest windows system in the world – the windowpane is attached to the frame by one or more side hinges. It can open both inwards and outwards, to the left or right, which allows maximum flow of air into the room. Heavily used in modern bungalows, hotels, hospitals, and buildings due to their high ventilation, noise attenuation, no rainwater ingress, dust-free properties.
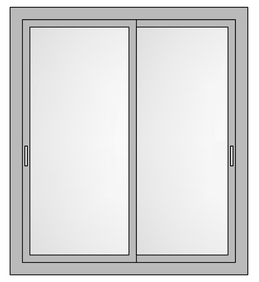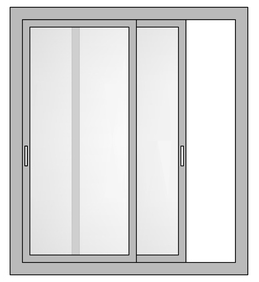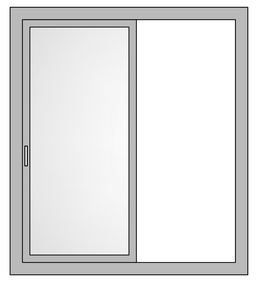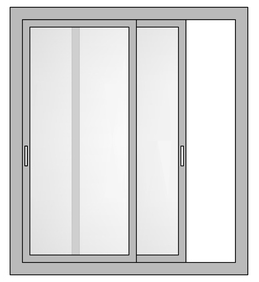
Slider Windows
The most common windows system across India – sliding windows comprises of two or more than two horizontal sashes that are fitted with rollers at the base for smooth sideward track movement. Preferred for residential and commercial spaces where space saving is a must. They offer ease of operations, low maintenance and more space.
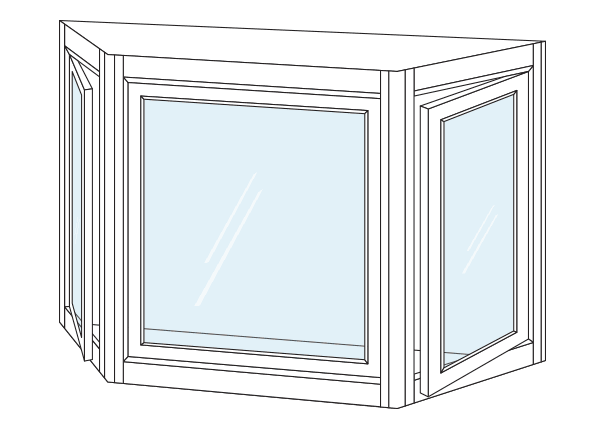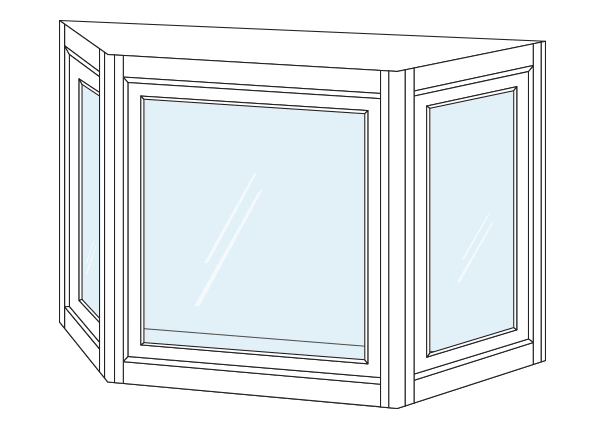
Bay / Coupled Windows
These windows are 2 or more windows, joined together with a Coupler or Baypole to form a particular shape and form. They generally, extend out of the walls to form a hollow bay. These are preferred for design elegance and space formations within the window area.
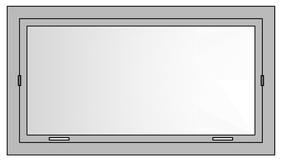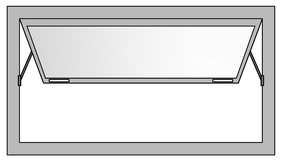
Awning Windows (Top Hung)
Like casement windows, these windows too have a hinged sash, but the hinges are at the top. These are not meant to be opened 100% as casements. Majorly used in Toilets, Kitchens, Stairs and Store areas where privacy and ventilation are a requirement.
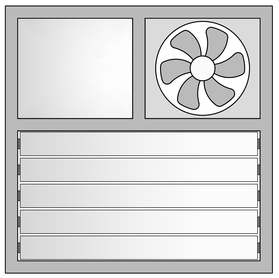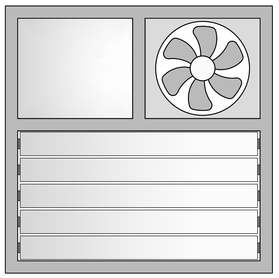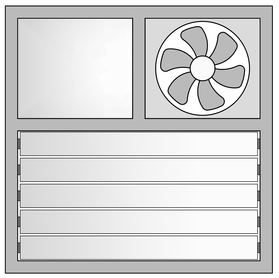
Louvers (Moveable / Fixed)
Strips of glass are fixed on a hardware on the frame of the window directly. There are no sashes on these windows. These windows are majorly used for Toilets and have only ventilation and privacy usage.

Tilt and Turn
These windows can tilt inwards for protection against rain and swing in like a casement window with the help of their side hinges. They are best suited when you need the slight ventilation but without the outside weather elements affecting your home. Ideal for homes in hilly and rainy areas.

Slide and Fold Doors
These are special doors – which give you 100% Openable space for movement however takes minimal stacking space for the sashes.
They operate on special hardware and are ideal for open Balconies and Lawns.

Tilt & Slide Doors
These windows can tilt inwards for protection against rain yet ventilate and slide like a slider system with the help of rollers. They always have 50% fixed for sturdiness. They are ideal for commercials like hotels, offices and hospitals that open out to lawns and gardens.
How to choose a particular Design and Style of Windows?
| Sound insulation | If you live in a crowded locality or close to busy roads, you might want to go for windows which offer superior sound insulation, so that you can have a peaceful environment at home. |
| Weather resistance | Like other aspects of the house, windows must be chosen keeping in mind the climatic conditions, altitude, etc. Especially if you are living in high-rise buildings or in heavy monsoon areas, it is imperative that windows withstand torrential rains and high-speed winds, thereby weatherproofing your home. Nowadays, with new-age framing materials like uPVC, it is even possible to construct UV resistant windows that neither fade, even under sustained exposure to sun, nor expand or contract with temperature variations. |
| Dust proofing | Dust proof windows are designed to be airtight, leaving no gaps to allow dust to enter. This enhances the quality of air in your home and ensures your interiors stay clean. |
| Energy efficiency | Windows play an important role in determining the energy costs of your home. Therefore, you should consider the following energy efficiency ratings of the window profile while deciding on your window solution |
| U-factor: ranging from 0.20 to 1.20, the lower the u-factor, the better the window traps heat inside the room. | |
| Solar heat gain coefficient (SHGC): it ranges from 0 to 1. The lower the number, the better the window blocks excess heat. | |
| Visible transmittance (VT): with a range of 0 to 1, it measures the amount of visible light allowed inside by the window. 1 indicates total visible transmittance, while 0 indicates complete opaqueness. | |
| An energy efficient window will not let outside heat flow in or cold-air escape out, as a result air-conditioning costs goes down | |
| Longevity & durability | Installing low-maintenance, weather-resistant and termite-proof windows will ensure your windows stay as good as new for a long time and even outlast the building |
| Beautify your home interiors | Windows no longer serve just utilitarian purpose but are important aesthetic elements that add to the beauty of your home. With technological advancements, windows of various sizes, shapes and styles are now possible. Choose the ones that complement the architectural style of your home |
| Save maintenance hassles | If you must get your windows repainted every few months, leading to a lot of unnecessary cost and discomfort, it is time to replace them with maintenance-free windows. These days windows made from special fade-resistant uPVC blends are widely available in the market. They do not require painting, just routine cleaning with soap and water. |
| Opt for convenience and optimize space usage | To combat challenges arising due to space constraints, it is best to replace two-way opening windows with sliding windows. Not only is this easy and smooth to operate, but it is also quite easy to clean. |
| Maintain privacy | Switching to a one-way view window is best suited for those who wish to avoid peeping eyes. One-way windows make it difficult for someone standing outside during the day, to see inside the home. |
| The right kind of installation | While the right windows can help to transform your living space, right installation is equally important. Windows with cracks or gaps, allow hot or cold air to enter the house, increasing the dependency on an air conditioner or heater. This increases your energy bills. It is recommended that you hire trained and certified installers to get your new windows in place. |






































